FOX (Food in a box) aims to rethink the way we process food. The project values sustainability and health while focusing on meeting consumer expectations towards local, qualitative foods. To achieve this, FOX uses mild processing technologies, such as pre-treatment before drying and mild preservation techniques like pulsed electric field (PEF). The use and advantages of PEF are explained in this article.
How does PEF technology work?
The technology can be used for different applications.
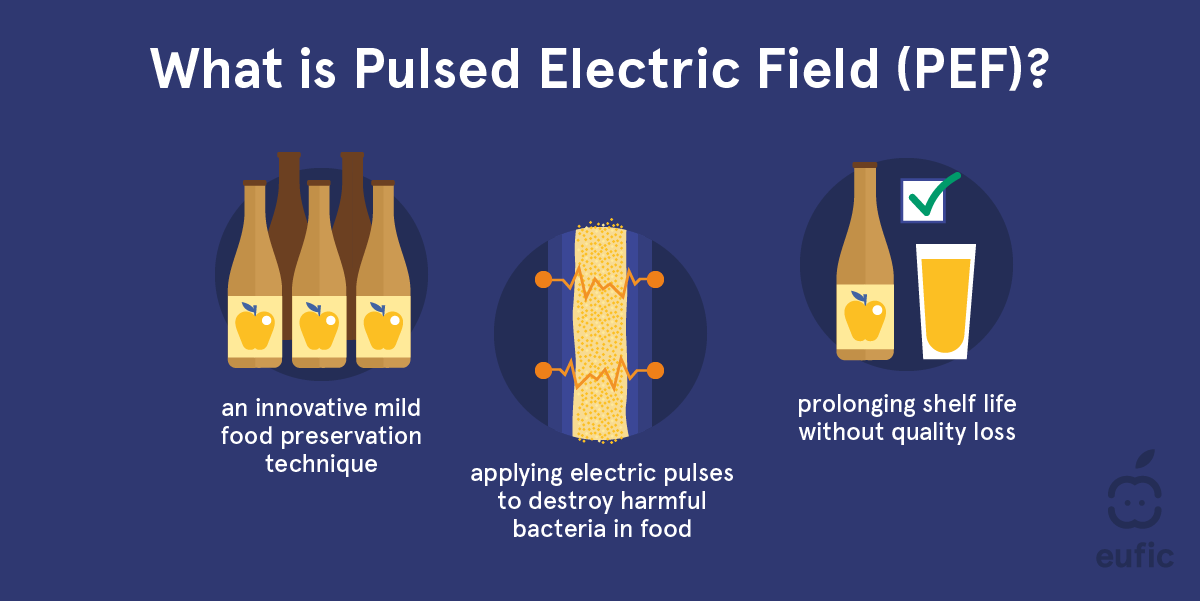
As an innovative mild food processing technology, PEF extends the shelf life and respects the food quality at the same time. Other commonly used processes using high temperature, such as heat pasteurisation, affect food quality more negatively.
The PEF mechanism is called electroporation and based on the following steps:1
- Very short electric pulses of high voltage are applied to the food.
- Small pores are formed in the cell membrane of the food by the electric pulses without damaging the cell compounds, such as vitamins.
Another application, where many advantages have been seen already is the pre-treatment for drying. PEF is creating small whole in the membrane of the biological cells causing an easier extraction of water. As a result, reduced process conditions in terms of temperature and time can be used for the drying process.2
When PEF is used for juice preservation, the electric pulses make pores in the cell of microorganisms such as Salmonella typhimurium or Escherichia coli and inactivate them. This way, fresh juice can be stored longer.1
When PEF is used for extraction, the pores in the cells make the content more easily accessible to produce for example puree or juice. 3
A short video from one of the project’s partners ELEA explains this mechanism:
How is the PEF technology used in FOX?
In the FOX project, the three application of the PEF technology will be used and tested in the different European regions (Food Circles):
- In Food Circle 1, which focus on juice processing, PEF will be used for the preservation of juice.
- In Food Circle 2, which focus on drying processing, PEF will be used as pre-treatment before drying to enhance retrieving water from fruit.
- In Food Circle 4, which focus on upscaling plant side streams, PEF will be used for extraction and preservation.
The PEF technology is relatively new, but it is already used by the juice industry in several countries. Project partners DIL and ELEA have successfully developed and realised PEF systems for low heat PEF preservation of liquids. They will now design and build a small-scale PEF unit suitable for on-farm use.
What are the benefits of PEF technology for food products?
- Higher food quality and nutritional value
For juice preservation, PEF is used at moderate temperature and serves as an alternative to heat pasteurisation (using high temperature). As a result, heat-sensitive nutrients, such as vitamins are less degraded.1
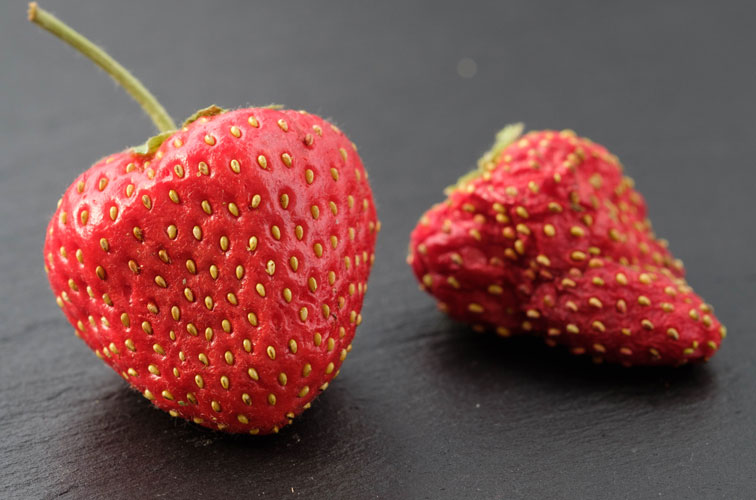
Compared to conventional processing methods, more pigments and antioxidants remain in the food product due to the shorter drying time with PEF.2 The dried food products have also better form, when receiving the PEF pre-treatment before.
Figure 1: Dried strawberry pre-treated with PEF on the left and not pre-treated on the right (Image: ELEA)
- Extended shelf life
By decreasing the pathogenic microorganisms in liquid products, fresh juice shelf life gets prolonged from some days to several months.1
- Keep the natural way of the product
There is no need to add preservatives, due to PEFs ability to inactivate microbes, or colourants, or aromas as these fruit compounds are retained during the PEF process.
Figure 2: Fruit juices treated with PEF technology and example of a PEF unit on an industrial scale (Image: ELEA)
What is the benefit of PEF technology for the environment?
As a low heat treatment for juice preservation, PEF uses less energy than conventional preservation methods. A study on apple juice reported that “the energy consumption could be reduced from above 100 to less than 40 kJ.kg−1.4
It is the same for drying, as the PEF pre-treatment allows the drying step to go faster, the consumption of energy for this step is naturally reduced.2
This short illustrative video made by the FieldFOOD project presents even more advantages of using the PEF technology in other food processing (e.g. facilitating the removal of fruits and vegetables peels or reducing the malaxation time in olive oil production).5
Read the page about the 4 Food Circles to discover the parts of the project where PEF technology is used.
References:
- Buckow R, Ng S & Toepfl S (2013). Pulsed Electric Field Processing of Orange Juice: A Review on Microbial, Enzymatic, Nutritional, and Sensory Quality and Stability. Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety 12: 455-467.
- Onwude D, et al. (2017). Non-thermal hybrid drying of fruits and vegetables: A review of current technologies. Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies 43:223‑238.
- ELEA GmbH (2017). ELEA GmbH Pulsed Electric Field Animation. Available on : https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wnZuLzhh0b8&feature=youtu.be
- Heinz V, Toepfl S & Knorr D (2003). Impact of temperature on lethality and energy efficiency of apple juice pasteurization by pulsed electric fields treatment. Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies 4(2):167-175
- EFFoST (2018). Advantages of using PEF technology in food processing. Available on: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=2z0uLS8oQ_I&feature=youtu.be






![FOX at FI [Food Ingredients] Europe](https://www.fox-foodprocessinginabox.eu/wp-content/uploads/2022/12/Screenshot-2022-12-13-131707.png)
